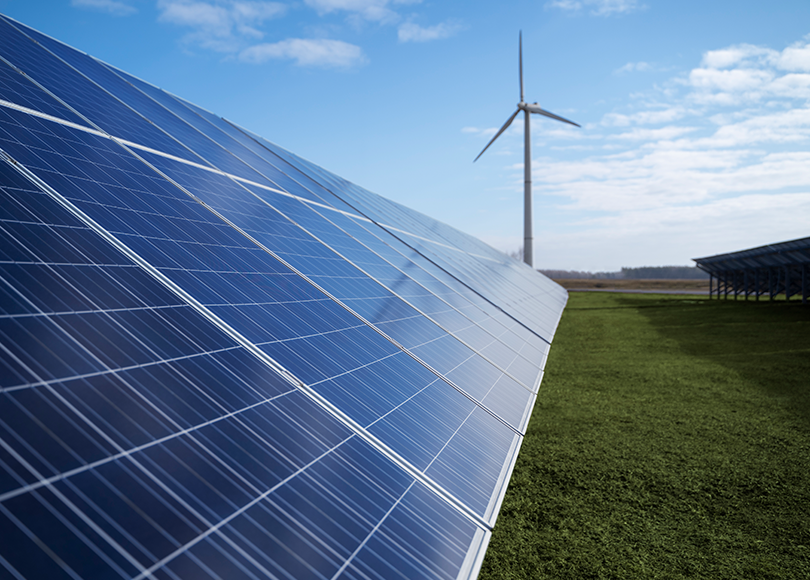

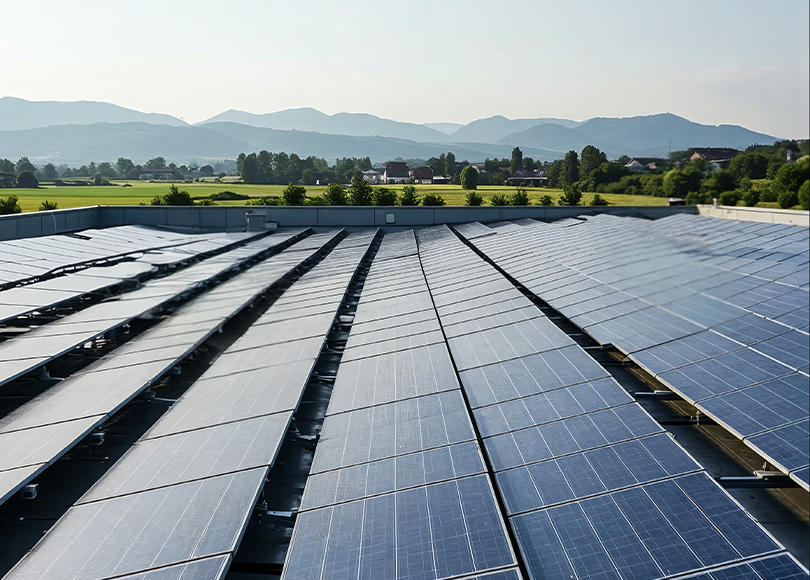
A ground-mounted solar Project is a solar power generation system where solar panels are installed on the ground instead of rooftops. These systems are typically deployed on large open land areas and are supported by structures that elevate the panels at an optimal angle to capture sunlight. Ground-mounted systems are ideal for areas with abundant land space and are commonly used in large-scale solar power plants to generate substantial amounts of electricity.
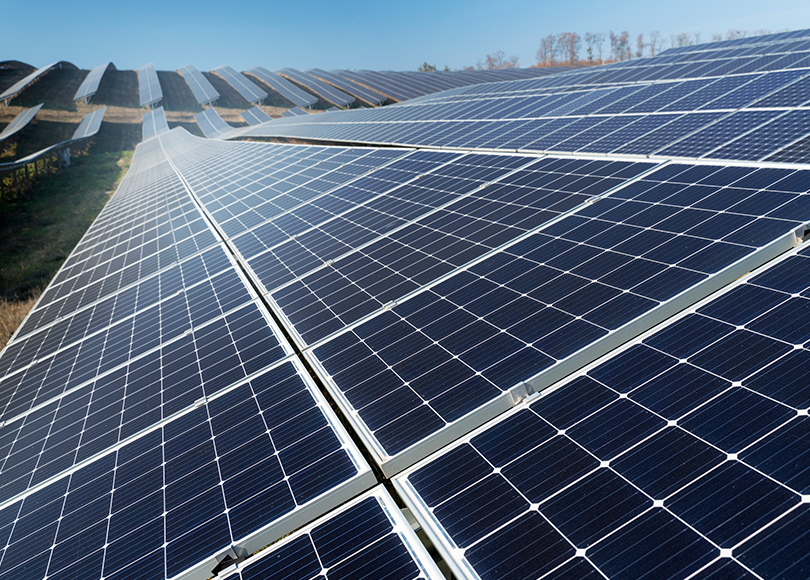
Ground-mounted systems maximize sun exposure, which is ideal for areas with limited rooftop space.
Ground-mounted systems maximize sun exposure, perfect for areas lacking sufficient rooftop space.

Ground-mounted systems are built to withstand harsh weather conditions and require minimal maintenance.

They can easily be installed on various unused spaces like rooftops, parking lots, or agricultural land.

Optimal sun exposure and efficient panel orientation can lead to higher energy production.

Durable construction ensures longevity with minimal maintenance, making it cost-effective.

This system can be installed on various land types, including flat, sloped, and uneven terrain.

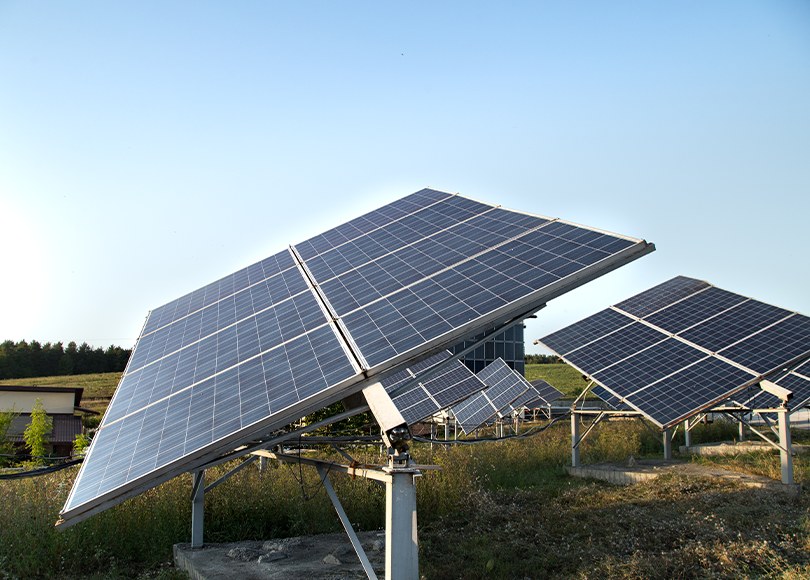
Some ground-mounted systems use trackers, enabling solar panels to follow the sun, boosting production.

Reduces carbon emissions and promotes the use of clean, sustainable energy sources.



Assistance with required approvals from government & local authorities.

Detailed feasibility analysis to ensure maximum efficiency.

Customized solar park designs tailored to site conditions.

Quality materials and seamless installation to ensure longevity.

Comprehensive support to maintain optimal performance.

Purpose : For factories or industries without sufficient rooftop space.
How It Works :
Generate solar power at a remote location.
Transmit electricity to your factory via the grid.
Pay minimal transmission and wheeling charges.
Benefits :
Green energy at your consumption site.
Reduced dependency on DISCOM rates.
Long-term energy cost savings.
Note :
Policies for captive use vary by state. Contact us for state-specific guidance.
Purpose : Sell solar energy directly to the government under programs like PM Kusum Yojana.
How It Works :
Participate in reverse bidding to determine the electricity rate.
Generate steady income by selling energy to DISCOM or government entities.
Benefits :
Attractive subsidy benefits under PM Kusum Yojana.
Secure investment model with long-term returns.
Note :
This model is highly popular among investors due to minimal risks and reliable returns.


Purpose : Sell solar energy directly to the government under programs like PM Kusum Yojana.
How It Works :
Participate in reverse bidding to determine the electricity rate.
Generate steady income by selling energy to DISCOM or government entities.
Benefits :
Attractive subsidy benefits under PM Kusum Yojana.
Secure investment model with long-term returns.
Note :
This model is highly popular among investors due to minimal risks and reliable returns.

Purpose : Investment opportunity for individuals or businesses.
How It Works :
Investors set up solar parks and sign Power Purchase Agreements (PPA) with private companies or factories.
Sell electricity at rates lower than DISCOM tariffs.
Benefits :
Recurring income for investors.
Buyers benefit from cheaper electricity.
Note :
Transmission charges apply, but the savings outweigh costs significantly.
A ground mounted solar power plant is a photovoltaic (PV) system installed directly on land, as opposed to rooftops. It consists of solar panels mounted on frames anchored to the ground, converting sunlight into electricity for grid or captive use
Typically, 4–5 acres of land are needed per megawatt (MW) for crystalline silicon technology. Thin film technology may require slightly more land
Traditional fixed-tilt ground-mount systems
Single-axis and dual-axis tracking systems (which follow the sun for higher output)
Ballasted systems (used where ground penetration is not possible)
Greater flexibility in orientation and tilt for optimal sunlight
Easier maintenance and cleaning
Scalability for large projects
No dependency on roof condition or space
Utility-scale ground mounted projects generally do not receive direct capital subsidies. However, various state-level incentives (like exemption from open access charges, feed-in tariffs, tax benefits, accelerated depreciation) may apply. Central support is sometimes available through schemes like VGF (Viability Gap Funding) in select tenders
Land identification and acquisition
Site assessment (soil, shading, wind, etc.)
System design and engineering
Regulatory approvals and grid connection
Procurement and installation
Commissioning and O&M setup
Ample unshaded land
Suitable soil and ground conditions
Proximity to grid infrastructure
Minimal environmental and legal constraints
Land acquisition and legal clearances
Grid connectivity and evacuation
Site-specific issues (soil, wind, dust, flooding)
Regulatory and policy changes
Solar panels typically last 25 years or more, with inverters and other components requiring replacement or maintenance during the plant’s life
Yes, each state may have its own solar policy, offering incentives, regulatory frameworks, and specific procedures for land use, grid connection, and tariffs